Petrochemical derivatives are products obtained from the processing of crude oil and natural gas, serving as intermediates or final products in various industries.
Naphtha is a flammable liquid hydrocarbon mixture, primarily used as a feedstock for petrochemical production (e.g., ethylene, propylene) and as a component in gasoline blending.
Applications: * Petrochemical Feedstock: Cracking to produce olefins (ethylene, propylene, butadiene) and aromatics (benzene, toluene, xylenes). * Gasoline Blending: Used as a high-octane component in gasoline. * Solvent: In paints, varnishes, and dry cleaning. * Hydrogen Production: Steam reforming for hydrogen production.

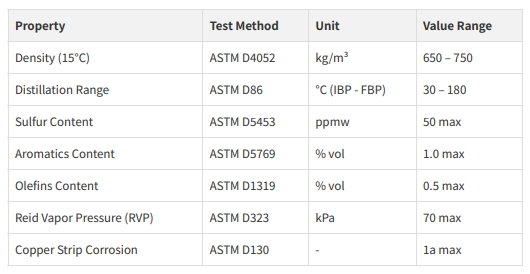
Note: Naphtha specifications vary widely depending on its source (e.g., paraffinic,
naphthenic, aromatic) and intended use. Petrosphere ensures that the naphtha
supplied meets the specific requirements for petrochemical cracking or gasoline
blending.
Gas condensate is a low density mixture of hydrocarbon liquids that are present as gaseous components in raw natural gas. It is often separated from the natural gas stream at the wellhead or in gas processing plants and can be used as a refinery feedstock or blended into crude oil.
Applications: * Refinery Feedstock: Processed in refineries to produce gasoline, jet fuel, diesel, and other refined products. * Petrochemical Feedstock: Used as a feedstock for steam crackers to produce olefins and aromatics. * Diluent: For heavy crude oil to reduce its viscosity for pipeline transportation.
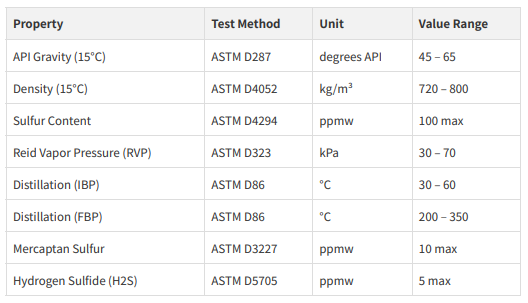
Note: Gas condensate specifications are highly dependent on the source field and
stabilization process. Petrosphere works closely with clients to ensure the condensate
meets their specific refinery or petrochemical plant requirements.